tear duct test|tear duct in eyes : broker The symptoms of a blocked tear duct can include: 1. Watery eyes (epiphora). 2. Gooey or crusty buildup on your eyelids or in your eyelashes. 3. Frequent rubbing of your eye or face around the blocked duct. 4. Redness and swelling (from rubbing). 5. Blurred vision. These blockages can also make it easier to . See more With Tenor, maker of GIF Keyboard, add popular Penelope P.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webMétodo 1. Removendo brincos com tarraxa de borboleta ou trava de segurança. Baixe em PDF. 1. Segure bem as duas partes do brinco, cada uma com uma mão. É importante .
The symptoms of a blocked tear duct can include: 1. Watery eyes (epiphora). 2. Gooey or crusty buildup on your eyelids or in your eyelashes. 3. Frequent rubbing of your eye or face around the blocked duct. 4. Redness and swelling (from rubbing). 5. Blurred vision. These blockages can also make it easier to . See more
Tear duct blockages can happen for a few different reasons. Some are congenital, meaning you have them when you’re born. Others develop later in life. See more
A blocked tear duct is just the kind of place where bacteria find it easy to grow, so bacterial infections or abscesses are the main possible complications of a . See more
Tests used to diagnose a blocked tear duct include: Tear drainage test. This test measures how quickly your tears are draining. One drop of a special dye is placed on the surface of each eye. You may have a blocked tear duct if after five minutes most of the dye is still on the surface of your eye. Irrigation and probing.
Treatments can widen or bypass a blocked tear duct to help tears drain normally out of your eye again. Opening up the ducts often eases symptoms like tearing, pain, and redness.
When tear ducts become blocked, tears build up. These irritate the eyes, increasing the risk of infection and causing painful swelling. Read more about blocked tear ducts here. A special fluid is flushed into the affected tear duct opening and, if the fluid cannot be tasted in the throat, a blocked tear duct is diagnosed. Other tests may include an X-ray or CT scan of the tear duct area (called a dacryocystogram). A tear osmolarity test. This type of test measures the composition of particles and water in your tears. With dry eye disease, there will be less water in your eyes. Tear samples to look for markers of dry eye . An estimated 20% of newborns come into this world with a blocked tear duct. This is referred to as a congenital blocked tear duct. In most cases, the condition usually resolves itself within four to six months—though if .
Loose skin cells or dirt that get lodged in the tear duct can block tears. Tumors in the nose can block the tear ducts, as can sarcoidosis or granulomatosis, inflammatory conditions that can cause swelling and prevent . See your doctor if your symptoms worsen. Physical examination by a medical professional is required in order to diagnose a blocked tear duct. While simple inflammation might be causing the blockage, it could also be a tumor or .Fluorescein dye can also be used to test whether the duct is free. However, syringing by itself rarely cures the blockage. If infection is the cause, antibiotic drops may be needed. . If surgery is needed, a new passage can be created between the tear sac (at the inner corner of the eye) and the inside of the nose; this can be done either .
This new route bypasses the duct that empties into your nose (nasolacrimal duct), which is typically the blockage site. Stents or intubation typically are placed in the new route while it heals, and then removed three or four months after surgery. The steps in this procedure will vary depending on your particular tear duct blockage. Dye disappearance test: This test uses dyed eye drops to determine if your tear ducts are blocked. If the eye drops disappear within 5 minutes, there’s no tear duct obstruction. A blockage in your tear duct causes dacryocystitis. These blockages disrupt the flow of tears from your eyes into your nasal cavity. A membrane that blocks the duct causes the blockage in newborns. In children and older people, blockages can be caused by many things. Dacryocystitis refers to an infection of the tear sacs, which are part of the tear drainage system in the eye. Tears drain from each eye through small canals (drainage canals), a tear sac, and a tear duct.Drainage canals are found at the inner corner of each upper and lower eyelid, and they carry away tears that have rinsed the front surface of the eye.
Dye disappearance test. Not always necessary, but used to test if tears are draining at proper rate (particularly for intermittent symptoms) . dye remains in eye (visible as a bright green tear meniscus) or escapes over eyelid to drain down cheek; Management. Initial observation vs. duct massage; Disposition. Follow up with primary care .
custom moisture meter for plants amazon
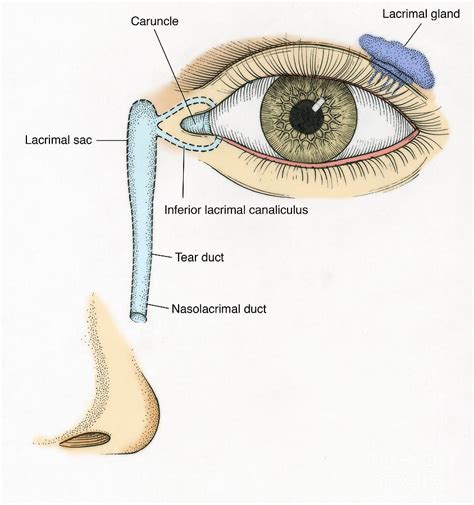
This sac leads to the tear duct, which goes around bony structures surrounding your nose and drains into your nasal cavity. Symptoms of a Blocked Tear Duct. Symptoms include: Tearing; Discharge from the eye; Pain at the tear duct or surrounding area; Causes of a Blocked Tear Duct In most cases, the cause of a blocked tear duct is not known.
A leading cause of blocked tear ducts in adults is infection of the eyes, tear duct system, or nasal passages. An injury or trauma to the eye can also lead to a blocked tear duct.Blocked tear ducts are a fairly common problem in infants. The earlier they're discovered, the less likely it is that infection will result or surgery will be necessary. . Sometimes they do a painless test using a dye to see if the tear duct is draining well. How Is a Tear-Duct Blockage Treated? Often a blocked tear duct clears up on its own .
what is a tear duct
In some dogs, this nasolacrimal duct can become obstructed, or blocked. Obstruction may result in tears overflowing and running out of the eye. This overflow of tears can lead to moisture and tear staining below the eye. The lower nasolacrimal duct is most commonly affected, and obstruction of the lower duct results in more clinically visible .Schirmer's test determines whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. This test is used when a person experiences very dry eyes or excessive watering of the eyes. . The dye should drain with the tears through the lacrimal duct into the nose within 2 minutes. If patients do not have enough tears to flush the dye into the nose . The nasolacrimal duct may even become infected. Blocked tear duct. A blocked tear duct occurs when the tear duct drainage system becomes obstructed. For example, the puncta sometimes narrow with age, which may .
The incidence of nasolacrimal duct obstruction is 20.24 per 100,000.[2] . (10 micrograms of TC-99) in the inferior fornix and tear flow with a scintigram gives physiological information of tear flow. The test involves . Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) or dacryostenosis is the most common disorder of the lacrimal system.[1] Approximately 6% to 20% of newborns patients present with some symptoms.[2] Typically, NLDO presents more often in the first weeks or months of life with symptoms beginning when normal tear production occurs, presenting as excessive tearing . They keep old tears from flooding your tear ducts constantly. Nasolacrimal duct (tear ducts): Nasolacrimal duct is the medical term for your tear ducts. Old tears that leave your eye through your lacrimal puncta and lacrimal sacs drain into tear ducts on either side of your nose. Your tear ducts empty into the back of your nose. Tear duct surgery is an effective, minimally invasive surgical option for people who require their blocked tear ducts to be reopened following blockage between the eye socket and nose. In our latest article, highly experienced Sheffield-based otolaryngologist, Mr Miran Pankhania provides an expert overview of what exactly tear duct surgery .
Common symptoms of a blocked tear duct include watery eyes and a sticky white or yellow discharge that can become crusty. Babies can be born with blocked tear ducts, but this often resolves on its own without treatment by one year of age. In adults, how you treat a blocked tear duct depends on what is causing the blockage.Tear duct massage can help open the blocked duct so tears can flow through it. How to Massage the Tear Duct. Wash your hands with soap and warm water before and after the massage. Place the tip of your index finger against the side of your child’s nose, in the corner of the eye with the blocked tear duct (Picture 2). Tear duct probing. If a tear duct doesn't open on its own by your baby's first birthday, the doctor can place a thin probe into the puncta to open the tissue covering the duct. Balloon catheter .
If your doctor suspects a blocked tear duct, a number of tests may be done to examine the tear drainage system and detect the exact location of the blockage. Tests used to diagnose a blocked tear duct include: Tear drainage test: This test measures how fast your tears can drain. A drop of a special dye is placed on the surface of each eye.A blocked tear duct is usually diagnosed based on a complete medical history and a physical examination of your child. Additional tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for a blocked tear duct. Specific treatment for a blocked tear duct will be determined by your child's healthcare provider based on: To confirm a blocked tear duct, the patient will undergo a few tests. Diagnostic Tests: Tear Drainage Test: As the name suggests, this test detects how fast the tears get drained. A drop of special dye is added near the tear duct. If it is seen after 5 minutes, tear duct blockage is confirmed.
The Jones 1 test is performed by instilling fluorescein into the conjunctival fornices and passing a cotton-tip into the inferior meatus near the valve of Hasner to recover the dye. . Paulsen, F. P., Thale, A. B., Hallmann, U. J., Schaudig, U. & Tillmann, B. N. The cavernous body of the human efferent tear ducts: function in tear outflow .You may need this surgery if your own tear duct has become blocked. For Patients For Providers Health Sciences University. 1-800-CEDARS-1 English. English. . Before you agree to the test or procedure make sure you know: The name of the test or procedure; The reason you are having the test or procedure .
tear duct in eyes
hole in tear duct
WEBC Eu sei que essa luta logo vai passar Bb Tá doendo, mas não vai querer parar Bb/D F Não deixe a esperança em você morrer Am7 C7 (4/9) Você precisa crer F Vai chegar a .
tear duct test|tear duct in eyes